Domestic Mutual Funds Invest in Their Overseas Counterparts:-
In the ever-evolving landscape of investment opportunities, mutual funds have become a cornerstone for many investors seeking diversification, professional management, and potential returns. As globalization continues to shrink the world and interconnect markets, one question that often arises is: Can domestic mutual funds invest in their overseas counterparts? This article explores the intricacies of such investments, the regulatory framework governing them, the potential benefits and risks, and how investors can navigate this complex terrain.
Understanding Mutual Funds and Their Investment Strategies
What are Mutual Funds?
Mutual funds are investment vehicles that pool money from multiple investors to purchase a diversified portfolio of securities, such as stocks, bonds, and other assets. Managed by professional fund managers, mutual funds offer several advantages, including diversification, liquidity, and accessibility to a broad range of asset classes.
Types of Mutual Funds
Mutual funds come in various forms, including equity funds, debt funds, hybrid funds, and sector-specific funds. Each type of mutual fund follows a distinct investment strategy, catering to different investor preferences and risk appetites.
The Concept of Overseas Investments by Mutual Funds
What Constitutes Overseas Investment?
Overseas investment refers to the practice of investing in foreign markets. For mutual funds, this can mean purchasing securities listed on foreign exchanges, investing in international companies, or even buying shares of overseas mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
Why Consider Overseas Investments?
There are several reasons why mutual funds might consider investing overseas:
- Diversification: Investing in international markets can provide diversification benefits, reducing the overall risk of the portfolio by spreading investments across different geographic regions and economies.
- Growth Opportunities: Emerging markets and developed economies outside the domestic market may offer significant growth potential, driven by different economic cycles, industry trends, and technological advancements.
- Currency Hedging: Overseas investments can act as a hedge against domestic currency fluctuations, providing additional stability to the portfolio.
- Access to Global Brands: Investing internationally allows exposure to leading global companies and brands that might not be accessible through domestic markets alone.
Regulatory Framework for Overseas Investments by Domestic Mutual Funds
Regulatory Authorities
In most countries, the mutual fund industry is regulated by a central authority to ensure transparency, protect investors, and maintain market stability. In India, for example, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is the primary regulatory body overseeing mutual funds and their investment practices.
Guidelines for Overseas Investments
Regulatory authorities typically set guidelines for mutual funds investing overseas to manage risk and ensure compliance. Key aspects of these guidelines may include:
- Investment Limits: Regulations often cap the amount mutual funds can invest in overseas assets. For instance, SEBI has stipulated that mutual funds in India can invest up to $7 billion collectively in overseas securities and up to $1 billion in overseas ETFs.
- Permitted Instruments: The types of overseas investments allowed might be specified, such as foreign stocks, bonds, ETFs, and mutual funds.
- Due Diligence: Mutual funds must conduct thorough due diligence and risk assessment before investing in foreign assets to ensure they align with the fund’s investment objectives and risk tolerance.
- Disclosure Requirements: Mutual funds are required to disclose their overseas investment strategies and holdings to investors, ensuring transparency and informed decision-making.
Potential Benefits of Investing in Overseas Mutual Funds
Enhanced Diversification
One of the primary benefits of investing in overseas mutual funds is enhanced diversification. By spreading investments across different countries and regions, mutual funds can reduce their exposure to domestic market risks and tap into a broader range of growth opportunities.
Access to High-Growth Markets
Investing in international markets allows to capitalize on high-growth opportunities in emerging economies. Countries like China, India, Brazil, and others have shown remarkable economic growth, driven by factors such as rapid industrialization, urbanization, and technological innovation.
Currency Diversification
Overseas investments provide exposure to foreign currencies, offering a natural hedge against domestic currency depreciation. This currency diversification can help stabilize returns and protect against currency-related risks.
Exposure to Global Companies
Many leading global companies are headquartered outside the domestic market. By investing in overseas investors can gain exposure to these multinational corporations, benefiting from their growth and profitability.
Risks Associated with Overseas Investments
Market Risk
Investing in overseas markets introduces additional market risks. Foreign markets can be volatile and subject to different economic cycles, political instability, and regulatory changes. These factors can impact the performance of overseas investments and add complexity to portfolio management.
Currency Risk
While currency diversification can be beneficial, it also introduces currency risk. Fluctuations in foreign exchange rates can affect the value of overseas investments, potentially leading to gains or losses independent of the underlying asset performance. 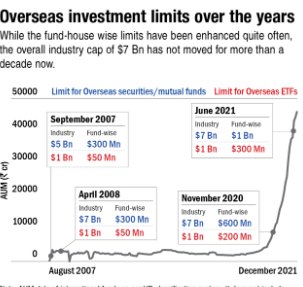
Regulatory and Compliance Risk
Navigating the regulatory landscape of foreign markets can be challenging. Different countries have varying regulations and compliance requirements that must adhere to, increasing the complexity of managing overseas investments.
Information and Monitoring Challenges
Accessing timely and accurate information about foreign markets and companies can be more difficult compared to domestic investments. This information asymmetry can affect the fund manager’s ability to make informed decisions and effectively monitor overseas investments.
Case Study: Indian Mutual Funds and Overseas Investments
SEBI’s Guidelines
In India, SEBI has allowed to invest in overseas markets within specified limits. This regulatory framework aims to balance the benefits of international diversification with the need to manage risks and protect investors.
Examples of Indian Mutual Funds Investing Overseas
Several Indian have incorporated overseas investments into their portfolios. For instance, some equity mutual funds invest a portion of their assets in global technology giants like Apple, Microsoft, and Alphabet, while others may invest in international ETFs to gain broad market exposure.
Performance and Impact
The performance of Indian with overseas investments has varied, reflecting the benefits and risks of international diversification. Funds that successfully navigate foreign markets and manage currency risks have provided investors with enhanced returns and diversification benefits.
How Investors Can Navigate Overseas Investments in Mutual Funds
Understanding the Investment Strategy
Investors should thoroughly understand the investment strategy, including its approach to overseas investments. Reviewing the fund’s prospectus, fact sheets, and performance reports can provide insights into how the fund manager selects and manages international assets.
Assessing Risk Tolerance
Before investing in with overseas exposure, investors should assess their risk tolerance and investment objectives. Overseas investments can introduce additional risks, and it’s essential to ensure that these align with the investor’s overall portfolio strategy and risk appetite.
Diversification within the Portfolio
Investors should consider how overseas investments fit within their broader portfolio. Proper diversification across asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions can help mitigate risks and enhance potential returns.
Monitoring Performance
Regularly monitoring the performance of mutual funds with overseas investments is crucial. Investors should stay informed about global market trends, economic conditions, and currency movements that could impact their investments.
Consulting Financial Advisors
Given the complexities of overseas investments, consulting with financial advisors or investment professionals can be beneficial. Advisors can provide personalized guidance, help assess risk, and recommend suitable mutual funds based on the investor’s financial goals and risk tolerance.
Conclusion: Embracing Global Opportunities with Caution
The ability of domestic mutual funds to invest in their overseas counterparts opens up a world of opportunities for diversification and growth. However, it also introduces additional complexities and risks that require careful consideration and management.
Regulatory frameworks, such as those set by SEBI in India, aim to strike a balance between enabling global investment opportunities and protecting investor interests. For investors, understanding the nuances of overseas investments, assessing their risk tolerance, and seeking professional advice are key steps to navigating this dynamic landscape successfully.
As the global economy continues to evolve, the interplay between domestic and international investments will likely become more intricate and significant. By staying informed and adopting a strategic approach, investors can harness the potential of global markets while safeguarding their financial future. ALSO READ:- ANC Faces Major Setback as South Africa Heads to Watershed Election 2024