1. Introduction
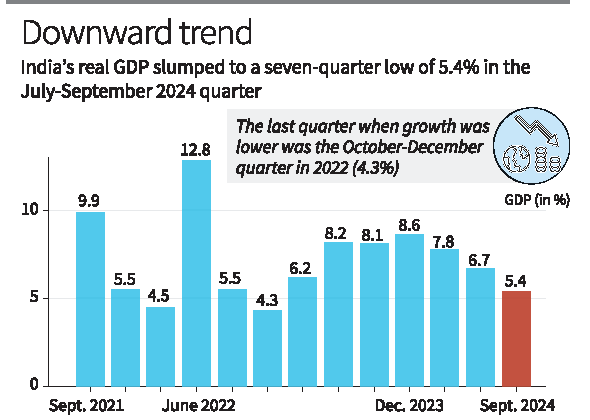
Road Ahead India’s GDP growth fell to 5.4% in the second quarter of the financial year, marking the lowest expansion in seven quarters. This figure, significantly below independent forecasts, Road Ahead underscores the challenges India’s economy faces in achieving the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) full-year growth target of 7.2%.
With sectors like agriculture and services showing resilience, others, including manufacturing and exports, Road Ahead reported a slump. Chief Economic Adviser (CEA) V. Anantha Nageswaran termed the performance a “one-off number,” but questions remain about the ability of the economy to rebound in the second half.
2. The Numbers Behind the Decline
The 5.4% growth rate falls sharply from 6.1% in the previous quarter and 7.8% in the same quarter last year. The slowdown is attributed to several factors:
- Manufacturing Weakness: Industrial output grew by a meager 1.9%, reflecting global demand challenges and domestic supply constraints.
- Export Decline: A slowing global economy dampened export performance, affecting GDP growth.
- Consumer Spending: Rising inflation and subdued rural demand curtailed consumer spending, Road Ahead a key growth driver.
- Investment Levels: Investment growth decelerated due to higher interest rates and global economic uncertainties.
3. Sectoral Performance Overview
3.1. Agriculture: A Lone Bright Spot
- The agriculture sector grew by 4.4%, supported by a strong monsoon and higher crop yields.
- Government schemes like PM-Kisan and enhanced rural infrastructure investment contributed positively.
3.2. Services Sector: Moderate Growth
- The services sector, which accounts for over 50% of GDP, expanded by 6.7%.
- Segments like IT services, finance, and real estate showed resilience, Road Ahead while hospitality and tourism lagged.
3.3. Industry and Manufacturing: Under Pressure
- The industrial sector contracted by 0.8%, reflecting weak demand and supply chain disruptions.
- Manufacturing output was hit hardest, declining by 1.2%, partly due to global headwinds and domestic uncertainties.
3.4. Construction and Infrastructure:
- Growth in construction moderated to 2.8%, affected by rising input costs and delayed project approvals.
4. Challenges Hindering Growth
4.1. Inflationary Pressures
- Persistent inflation, driven by high food and energy prices, Road Ahead Road Ahead has eroded household purchasing power.
- Elevated costs have also impacted corporate profit margins and curtailed investment appetite.
4.2. Global Economic Slowdown
- Recession fears in developed markets like the U.S. and Europe have weakened demand for Indian exports.
- Trade disruptions caused by geopolitical tensions, including the Russia-Ukraine conflict, Road Ahead Road Ahead continue to pose challenges.
4.3. Rising Interest Rates
- The RBI’s monetary tightening to control inflation has increased borrowing costs, Road Ahead dampening investment and consumption.
4.4. Sluggish Rural Demand
- Uneven monsoon distribution and rising rural debt levels have constrained rural spending.
- The rural economy’s recovery remains slower than anticipated.
5. Government’s Response and Policy Measures
5.1. Fiscal Stimulus
- The government has announced higher capital expenditure to boost infrastructure and create jobs.
- Schemes like PLI (Production-Linked Incentive) aim to attract private investment in key sectors like electronics and pharmaceuticals.
5.2. Inflation Management
- Measures to moderate inflation include food grain distribution through PMGKAY and reducing import duties on essential commodities.
5.3. Support for MSMEs and Startups
- Enhanced credit access for MSMEs through initiatives like the Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS).
- Startup incentives to foster innovation and employment generation.
5.4. Trade Agreements
- The government is actively pursuing free trade agreements (FTAs) to boost exports and diversify trade partners.
6. Expert Opinions on the Slowdown
- Chief Economic Adviser (CEA) Nageswaran: He called the GDP slowdown a “one-off number” and expressed confidence in a strong second-half recovery.
- RBI Projections: The central bank remains optimistic about achieving 7.2% growth for the fiscal year, emphasizing resilience in core economic indicators.
- Economists: Analysts have flagged concerns about sustained inflation and global risks, Road Ahead warning that the GDP target could be missed without aggressive reforms.
7. The Way Forward: Strategies for Recovery
7.1. Boosting Domestic Demand
- Strengthening rural incomes through enhanced agricultural subsidies and rural employment schemes.
- Promoting affordable housing and consumer financing to encourage spending.
7.2. Reviving Industrial Output
- Introducing sector-specific incentives to support manufacturing and reduce dependency on imports.
- Encouraging private-public partnerships for infrastructure development.
7.3. Diversifying Exports
- Expanding trade in emerging markets like Africa and Southeast Asia to mitigate dependence on Western economies.
- Promoting high-value sectors like IT, pharmaceuticals, and renewable energy for export growth.
7.4. Accelerating Reforms
- Implementing labor and land reforms to enhance ease of doing business.
- Streamlining GST compliance and reducing tax burdens for MSMEs.
7.5. Strengthening Social Welfare Programs
- Expanding health and education investments to improve human capital and productivity.
- Addressing income inequalities through targeted subsidies and direct benefit transfers.
8. Potential for Recovery in the Second Half
Despite the current slowdown, several factors could support a rebound in the coming quarters:
- Festive Season Boost: Increased consumer spending during the festive season.
- Global Recovery: A potential stabilization in global economic conditions could improve export demand.
- Policy Effectiveness: Timely implementation of government reforms and fiscal stimulus measures.
9. Conclusion
India’s 5.4% GDP growth in Q2 highlights both the resilience and vulnerabilities of its economy. While sectors like agriculture and services offer hope, challenges in manufacturing, exports, Road Ahead Road Ahead and rural demand need urgent attention.
The road to achieving the RBI’s 7.2% growth target will require coordinated efforts, Road Ahead including fiscal prudence, infrastructure investments, Road Ahead and structural reforms. With robust policy action and global recovery, India has the potential to navigate this slowdown and regain its growth momentum. ALSO READ:- Keir Starmer Criticizes Conservatives for “Open Borders Experiment” in Immigration Policy 2024
1win партнёрка 1win партнёрка .
мостбет официальный сайт мостбет официальный сайт .
официальный сайт 1win официальный сайт 1win .
1win кыргызстан https://1win6001.ru/ .
мостбет вход мостбет вход .
1win вход в личный кабинет https://1win6001.ru/ .
1wiun http://familyclub.borda.ru/?1-6-0-00002163-000-0-0-1743051813/ .
1вин сайт официальный https://familyclub.borda.ru/?1-6-0-00002163-000-0-0-1743051813/ .
1 win. 1 win. .
1вин приложение 1вин приложение .
1win партнерка вход alfatraders.borda.ru/?1-0-0-00004932-000-0-0-1743258210 .
зайти в 1вин http://www.balashiha.myqip.ru/?1-12-0-00000437-000-0-0-1743258848 .
бк 1win http://alfatraders.borda.ru/?1-0-0-00004932-000-0-0-1743258210 .
1вин официальный сайт мобильная balashiha.myqip.ru/?1-12-0-00000437-000-0-0-1743258848 .
партнёрка 1win https://alfatraders.borda.ru/?1-0-0-00004932-000-0-0-1743258210/ .
1вин про 1win6049.ru .
1win официальный сайт http://1win6049.ru/ .
1vin 1vin .
1 вин. http://1win6049.ru .
1 win регистрация https://balashiha.myqip.ru/?1-12-0-00000437-000-0-0-1743258848/ .
1win.kg https://alfatraders.borda.ru/?1-0-0-00004932-000-0-0-1743258210 .
1win официальный 1win официальный .
мостбет мобильная версия скачать svstrazh.forum24.ru/?1-18-0-00000136-000-0-0-1743260517 .
1вин официальный 1win6050.ru .
мотбет svstrazh.forum24.ru/?1-18-0-00000136-000-0-0-1743260517 .
1вин официальный мобильная 1win6050.ru .
один вин официальный сайт https://obovsem.myqip.ru/?1-9-0-00000059-000-0-0-1743051936/ .
1win бк http://obovsem.myqip.ru/?1-9-0-00000059-000-0-0-1743051936 .
1 вин вход в личный кабинет obovsem.myqip.ru/?1-9-0-00000059-000-0-0-1743051936 .
1 win регистрация https://obovsem.myqip.ru/?1-9-0-00000059-000-0-0-1743051936 .
mostber https://svstrazh.forum24.ru/?1-18-0-00000136-000-0-0-1743260517/ .
mostbet apk скачать mostbet apk скачать .
1 win kg https://1win6050.ru .
1win личный кабинет http://1win6051.ru/ .
1win партнёрка http://1win6051.ru/ .
1win online http://www.1win6052.ru .
1win.kg https://www.1win6052.ru .
Для максимально быстрого продвижения вверх по карьере требуется наличие официального диплома ВУЗа. Приобрести диплом университета у проверенной организации: freediplom.com/kupit-diplom-v-samare-bistro-i-bez-lishnix-zatrat/
1vin 1vin .
теплый склад для хранения личных вещей москва теплый склад для хранения личных вещей москва .
1 ван вин http://1win6052.ru/ .
мостбет авиатор https://www.mostbet6029.ru .
1win официальный сайт скачать http://www.1win6053.ru .
мостбет http://mostbet6029.ru .
1win online https://1win6053.ru .
1вин. http://www.1win6053.ru .
1vin pro http://1win6053.ru/ .
cod promoțional 1win cod promoțional 1win .
portofele electronice casino http://1win5011.ru/ .
jocuri de noroc online moldova 1win5011.ru .
1win kg скачать 1win kg скачать .
один вин один вин .
1win website http://1win15.com.ng .
1wi http://www.1win6009.ru .
скачать мостбет https://www.mostbet6012.ru .
мрстбет http://www.mostbet6012.ru .
1win зайти http://1win6009.ru .
скачат мостбет http://mostbet6012.ru .
mostbet игры https://www.mostbet6012.ru .
игра 1вин http://1win6046.ru .
Заказать диплом о высшем образовании!
Мы предлагаем документы институтов, которые расположены в любом регионе Российской Федерации. Дипломы и аттестаты выпускаются на “правильной” бумаге самого высшего качества: jobsantigua.com/employer/aurus-diploms
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по приятным тарифам.– fastdiploms.com/kupit-diplom-s-zaneseniem-v-reestr-bistro-i-nadezhno-11/
Мы изготавливаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и любых других профессий по приятным тарифам.– poluchidiplom.com/kupit-diplom-s-zaneseniem-v-reestr-v-rossii/
Заказать диплом института по доступной цене вы сможете, обращаясь к надежной специализированной компании. Мы оказываем услуги по производству и продаже документов об окончании любых ВУЗов Российской Федерации. Заказать диплом университета– diplomh-40.ru/kupit-diplom-zanesennij-reestr-6/
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по выгодным ценам. Купить диплом в Белгородской области и городе Белгород — kyc-diplom.com/geography/belgorod.html
Заказать диплом института по невысокой стоимости возможно, обратившись к проверенной специализированной фирме. Мы оказываем услуги по изготовлению и продаже документов об окончании любых ВУЗов России. Приобрести диплом любого университета– diplom-top.ru/kupit-realnij-diplom-o-visshem-obrazovanii-5/
Приобрести диплом университета по невысокой цене можно, обратившись к проверенной специализированной фирме. Мы предлагаем документы об окончании любых ВУЗов Российской Федерации. Приобрести диплом любого ВУЗа– diplom-kaluga.ru/kupit-diplom-s-otzivami-bez-xlopot-legko-i-bistro/
продамус промокод скидка на подключение продамус промокод скидка на подключение .
промокод продамус промокод продамус .
Приобрести диплом любого ВУЗа!
Приобрести диплом ВУЗа по доступной стоимости можно, обращаясь к проверенной специализированной компании. Купить диплом о высшем образовании: diplomg-cheboksary.ru/kupite-nadezhnij-diplom-sejchas-proverennoe-kachestvo
Мы можем предложить дипломы любых профессий по разумным ценам.
Вы приобретаете диплом через надежную компанию. Заказать диплом института– http://animalplanetnews.ru/dokumentyi-ob-obrazovanii-bez-problem-oformlenie-diplomov/ – animalplanetnews.ru/dokumentyi-ob-obrazovanii-bez-problem-oformlenie-diplomov
Покупка документа о высшем образовании через качественную и надежную фирму дарит массу плюсов для покупателя. Такое решение дает возможность сэкономить время и серьезные финансовые средства. Впрочем, плюсов намного больше.Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии. Дипломы изготавливаются на оригинальных бланках. Доступная цена по сравнению с крупными затратами на обучение и проживание. Приобретение диплома об образовании из российского ВУЗа станет рациональным шагом.
Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании: diplomc-v-ufe.ru/pokupka-diplomov-s-reestrom-4/
Приобрести диплом института по доступной стоимости вы можете, обращаясь к надежной специализированной компании. Мы предлагаем документы об окончании любых ВУЗов России. Купить диплом ВУЗа– bahchisaray.org.ua/index.phpshowtopic=35980
продамус промокод скидка продамус промокод скидка .
Где приобрести диплом по нужной специальности?
Полученный диплом со всеми печатями и подписями 100% отвечает условиям и стандартам, неотличим от оригинала – даже со специальным оборудованием. Диплом о высшем образовании – не проблема! ks4yumuo.listbb.ru/viewtopic.phpf=18&t=1617
Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании!
Мы предлагаем дипломы любых профессий по выгодным ценам. Вы заказываете документ через надежную фирму. : ukrom.in.ua/users/327wid=9340
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по приятным ценам.– forcemajor.maxbb.ru/viewtopic.phpf=7&t=1366
промокод продамус на 5000 promokod-prod.ru .
продамус промокоды продамус промокоды .
пластиковые окна дешево пластиковые окна дешево .
пластиковые окна дешево пластиковые окна дешево .
окна пвх окна пвх .
Где приобрести диплом специалиста?
Заказать диплом университета по доступной цене возможно, обратившись к проверенной специализированной фирме.: diplom-zakaz.ru
Мы можем предложить дипломы любых профессий по разумным тарифам. Дипломы изготавливаются на настоящих бланках Купить диплом о высшем образовании diplomp-irkutsk.ru
криптовалюты криптовалюты .
Мы готовы предложить дипломы любых профессий по выгодным тарифам. Цена зависит от выбранной специальности, года получения и образовательного учреждения: krasnozovodsk.flybb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=618
пластиковые окна под ключ цены пластиковые окна под ключ цены .
заказать пластиковые окна в москве заказать пластиковые окна в москве .
заказать пластиковые окна от производителя недорого http://www.1okno-krasnodar.ru .
теплые склады для хранения вещей https://veshi-hranenie.ru/ .
аренда боксов для хранения вещей москва аренда боксов для хранения вещей москва .
Заказать диплом о высшем образовании. Изготовление диплома занимает намного меньше времени, а стоимость при этом доступна каждому. Таким образом вы сможете сберечь деньги и время и найти хорошую работу мечты. Заказать диплом под заказ в столице можно через сайт компании. – polegasm.net/index.php/forum/welcome-mat/152520
купить пластиковые окна купить пластиковые окна .
Заказать диплом о высшем образовании!
Покупка диплома через качественную и надежную фирму дарит массу достоинств для покупателя. Заказать диплом любого ВУЗа у сильной организации: doks-v-gorode-severodvinsk-29.online
окна rehau москва 02stroika.ru .
https://l-spb.ru
https://tonersklad.ru
https://ancientcivs.ru
Заказать диплом любого университета поможем. Купить аттестат в Смоленске – diplomybox.com/kupit-attestat-v-smolenske
https://mirka-master.ru/kupit-plastikovye-okna-v-sankt-peterburge-nadyozhnoe-reshenie-ot-kompanii-afina-okna/
one win app login http://www.1win-apk.pro .
Где приобрести диплом специалиста?
Купить диплом университета по доступной стоимости возможно, обращаясь к проверенной специализированной компании.: institute-diplom.ru
Мы готовы предложить дипломы любой профессии по разумным ценам. Дипломы изготавливаются на подлинных бланках Заказать диплом любого университета diplomg-kurerom.ru
Где приобрести диплом специалиста?
Готовый диплом с приложением целиком и полностью отвечает запросам и стандартам Министерства образования и науки, неотличим от оригинала. Диплом о среднем образовании – легко! dely.nl/kupit-diplom-gosudarstvennogo-obrazca-344-2
1win aviator game download apk http://www.1win-apk.pro/ .
1 win apk download 1 win apk download .
Thanks for the article https://l-spb.ru/
For more information https://millionigrushek.ru .
betwinner online casino betwinner online casino .
betwinner app download 2023 http://www.betswinner.bet .
купить шкаф в подземный паркинг купить шкаф в подземный паркинг .
шкаф в паркинг в москве шкаф в паркинг в москве .
betwinner app betwinner app .
купить диплом в кургане купить диплом в кургане .
my-caffe.ru .
банкротство физлиц http://www.bankrotstvo-fiz-lic-moscow.ru .
kreativ-didaktika.ru .
For more information https://up-top.ru .
For more information https://tonersklad.ru .
купить аттестат школьный купить аттестат школьный .
банкротство физ лиц банкротство физ лиц .
Где приобрести диплом специалиста?
Заказать диплом университета по доступной цене возможно, обратившись к проверенной специализированной компании.: peoplediplom.ru
Где заказать диплом с архивной записью без посредников? Кликнуть сюда
В 2025 году наличие диплома всё ещё остаётся основным фактором при приёме на работу, повышении по службе или получении лицензии. И если у вас нет необходимого документа — это не повод терять время на долгие годы учебы.
✅ Выход есть — заказ диплома, полностью соответствующего оригиналу:
С печатями, подписями, голограммами,
С занесением в архив (по запросу),
Любой ВУЗ, колледж — по всей России и СНГ.
Кому может пригодиться?
Вас выгнали, но обучение практически завершено?
Нашли перспективную работу, но нет “корочки”?
Нужен диплом для лицензирования, повышения, тендера?
Мы работаем без предоплаты (по договору или поэтапно) и гарантируем полную конфиденциальность. У нас нет шаблонов — каждый документ готовится индивидуально, с учётом всех нюансов.
Наши гарантии:
Диплом, неотличимый от оригинала
Настоящие данные выпускника (по вашей анкете)
Быстрая и надежная доставка по России и СНГ
Юридически грамотно оформленный договор (по желанию)
Мы сотрудничаем с квалифицированными специалистами, которые знают, как должен выглядеть официальный документ — вплоть до мельчайших деталей. У нас много лет опыта и более random00..3999] довольных клиентов.
банкротство физлиц http://www.bankrotstvo-grajdan.ru .
окна пвх окна пвх .
Мы оказываем услуги по производству и продаже документов об окончании любых университетов РФ. Документы производятся на фирменных бланках. agapeplus.sg/employer/radiplomy
ипотека под мат капитал crediteurasia.ru .
аттестат за 9 класс купить arus-diplom6.ru .
ипотека под материнский капитал crediteurasia.ru .
Приобрести диплом любого ВУЗа!
Приобретение подходящего диплома через проверенную и надежную фирму дарит ряд преимуществ. Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании у сильной компании: doks-v-gorode-moskva-77.ru
Рекомендую услуги проверенных хакеров. Обращался, сделали все быстро и качественно – Услуги настоящих хакеров .
Заказывал услуги проверенного хакера. КОНТАКТЫ СПЕЦИАЛИСТА:
XakVision@protonmail.com
Рекомендую xakerforum.com/topic/282/page-6 .
Заказывал услуги проверенного хакера. КОНТАКТЫ СПЕЦИАЛИСТА:
XakVision@protonmail.com
Рекомендую xakervip.com/topic/282/page/10/ .
заказать пластиковые окна заказать пластиковые окна .
окна рехау москва окна рехау москва .
окна в москве http://02stroika.ru/ .
окна на заказ окна на заказ .
Рекомендую проверенного хакера – Запись звонков Почта специалиста: Unitstels@yandex.com
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://yarus-kkt.ru/
окна rehau окна rehau .
бесплатная накрутка подписчиков Бесплатная накрутка подписчиков.
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://yarus-kkt.ru/
накрутка реакций в телеграм Накрутка реакций в Телеграм.
Thanks for the article. Here is a website on the topic – https://40-ka.ru/
Thanks for the article. Here is a website on the topic – https://40-ka.ru/
Thanks for the article. Here is a website on the topic – https://kanunnikovao.ru/
Thanks for the article. Here is a website on the topic – https://kanunnikovao.ru/
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://mehelper.ru/
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://yarus-kkt.ru/
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://mehelper.ru/
проверика организации http://proverit-kontragenta.ru .
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://yarus-kkt.ru/
Here’s more on the topic https://bediva.ru/
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://orenbash.ru/
Here’s more on the topic https://bediva.ru/
Here’s more on the topic https://kinocirk.ru/
купить диплом о средне специальном образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом о средне специальном образовании с занесением в реестр .
Here’s more on the topic https://kinocirk.ru/
как купить диплом с проводкой как купить диплом с проводкой .
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://up-top.ru/
Here’s more on the topic https://kinocirk.ru/
купить аттестат 11 классов за 2002 год купить аттестат 11 классов за 2002 год .
заказать окна пвх alfa-okno.ru .
Here’s more on the topic https://voenoboz.ru/
легально купить диплом о легально купить диплом о .
mp3 скачать mp3 скачать .
Хочу порекомендовать пофессионального хакера. Справился отлично! Заказывал – Взлом страниц Почта специалиста: Unitstels@yandex.com
купить диплом проведенный москва https://arus-diplom33.ru/ .
Хочу поделиться положительным отзывом о хакере – Также рекомендую вам почитать по теме – https://telegra.ph/Moj-opyt-obrashcheniya-k-hakeram-07-30-4 .
И еще вот – https://telegra.ph/Opyt-obrashcheniya-k-uslugam-hakerov-Poleznyj-otzyv-07-30-2 .
Advantageous offer http://www.lazare.ru/content/view/20687/2/ .
купить аттестат за 10 11 класс отзывы http://www.arus-diplom25.ru .
заказать окна пвх http://www.1-stroymarket.ru/ .
купить аттестат за 11 классов в уфе купить аттестат за 11 классов в уфе .
диплом с проведением купить диплом с проведением купить .
Также рекомендую вам почитать по теме – https://dzen.ru/a/Z5Kjl5vfXxy5sEvX .
И еще вот – https://dzen.ru/a/Z5Pjbmv_MAqp42Bp .
Je recommande code promo 1xbet cote d’ivoire
Также рекомендую вам почитать по теме – https://dzen.ru/a/Z5O3BhGz7yMummPD .
И еще вот – https://dzen.ru/a/Z5KUIWfrv2sfumtD .
Рекомендую – https://ipodtouch3g.ru/metizy-vidy-naznachenie-i-kak-vybrat/
Thanks for the article https://ipodtouch3g.ru/
Here is another site on the topic https://photo-res.ru/
Here is another site on the topic https://photo-res.ru/
Рекомендую – https://med-like.ru/kak-nachat-uspeshnuyu-kareru-v-eskort-uslugah-s-agentstvom-rubus24-polnoe-rukovodstvo/
Рекомендую – https://med-like.ru/kak-nachat-uspeshnuyu-kareru-v-eskort-uslugah-s-agentstvom-rubus24-polnoe-rukovodstvo/
Thanks for the article https://rankva.com/increase-ahrefs-dr-moz-da-and-majestic-tf-with-seo-backliks-2786/ .
Thanks for the article https://www.irakly.info/post1010024.html#p1010024 .
Thanks for the article https://www.lovecrafts.com/en-gb/user/Grom95/851e1bd1-416c-4f2f-a0da-291fa0cea22e .
Thanks for the article https://www.pexels.com/@miha-mazur-2154731392/ .
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Luchshij-lajtovyj-spinning-TOP-modelej-dlya-legkoj-lovli-01-13 .
Thanks for the article https://telegra.ph/Luchshie-polyarizacionnye-ochki-dlya-rybalki-Top-10-modelej-01-13 .
Thanks for the article https://www.freeboard.com.ua/forum/viewtopic.php?pid=980487#p980487 .
Thanks for the article https://photozou.jp/wall/show/3419603 .
Thanks for the article https://hallbook.com.br/posts/616962 .
Thanks for the article https://mir-mamy.com.ua/forum/viewtopic.php?p=18764#18764 .
Thanks for the article https://bc39.unoforum.pro/?1-0-0-00004667-000-0-0-1721660606 .
Thanks for the article https://donbassforum.net/flud/topic-t3084260.html .
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
Website https://amurplanet.ru/ .
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
Website https://beksai.ru/ .
Website – http://fabnews.ru/forum/showthread.php?p=107786#post107786 .
Website – https://lostfiilmtv.ru/
Website https://jennifer-love.ru/metizy-klyuchevye-harakteristiki-i-rekomendatsii-po-vyboru/
Website https://jennifer-love.ru/
Website https://jennifer-love.ru/
Website https://ipodtouch3g.ru/ .
Website https://photo-res.ru/ .
Website https://portalbook.ru/arenda-avtomobilya-dlya-povsednevnyh-zadach-i-poezdok-po-gorodudlya-povsednevnyh-zadach-i-poezdok-po-gorodu/
Website https://portalbook.ru/arenda-avtomobilya-dlya-povsednevnyh-zadach-i-poezdok-po-gorodudlya-povsednevnyh-zadach-i-poezdok-po-gorodu/
промокоды на сегодня
промокоды на сегодня
промокоды сегодня
промокоды сегодня
промокоды на сегодня
промокоды сегодня
промокоды сегодня
промокоды на сегодня
La información más útil sobre cirugía urológica avanzada está disponible en la Clínica de Urología Moderna sin salir de casa.
En la Clínica de Urología Moderna se recopila la información clave sobre exámenes urológicos más habituales.
Todo lo que un hombre debe saber antes de operarse lo explican los especialistas de la Clínica de Urología Moderna.
лучшие отели в России
лучшие бутик-отели Москвы
лучшие отели в Тульской области
En un solo recurso, la Clínica de Urología Moderna ofrece detalles sobre estudios, cirugías y tratamientos médicos.
лучшие экскурсии во Вьетнаме
kraken зеркало рабочее
кракен маркетплейс официальный сайт
кракен маркетплейс
кракен ссылка
kraken обход блокировки
kraken маркетплейс зеркало