Retail Credit Growth recent years, retail credit growth has been one of the pillars of the global economy, driving consumer spending and contributing to overall financial health. However, the June quarter of 2024 has shown signs of cooling off, according to the latest data from TransUnion. This slowdown in retail credit growth has raised concerns among financial experts, economists, and policymakers. In this article, we will delve into the key aspects of this phenomenon, explore the reasons behind the deceleration, analyze the impact on consumers and businesses, and offer insights into what the future holds.
The Context: What is Retail Credit Growth?
Retail credit refers to the loans and credit facilities extended to individual consumers, which include personal loans, credit cards, mortgages, auto loans, and retail store financing. The retail credit growth rate is a critical indicator of the health of consumer spending, as it reflects the willingness and ability of consumers to borrow and spend money.
In recent years, many economies have experienced robust retail credit growth, supported by low-interest rates, rising incomes, and an increasingly credit-driven consumer culture. However, recent data from TransUnion’s June quarter report reveals a different narrative—one of cooling growth, signaling a potential shift in the dynamics of consumer credit markets.
TransUnion Report Overview
The TransUnion report for the June quarter of 2024 highlighted a significant slowdown in retail credit growth across several major economies. The data reveals that while credit growth is still positive, the pace of growth has decelerated considerably compared to previous quarters.  For the more information click on this link
For the more information click on this link
Key findings from the TransUnion report include:
- Decline in Credit Card Issuance: The report shows a noticeable decline in the number of new credit cards issued during the June quarter. This decrease is largely attributed to tighter lending standards by financial institutions and a more cautious approach by consumers.
- Personal Loan Growth Slows: Personal loan originations also saw a decline, with fewer consumers opting for unsecured loans. Rising interest rates and concerns over economic uncertainty have played a role in this trend.
- Mortgage and Auto Loan Growth Weakens: Mortgage and auto loan growth, two key components of retail credit, also experienced a slowdown. Higher interest rates and affordability issues in the housing market contributed to the weakening demand for mortgage loans, while rising vehicle prices affected auto loan growth.
Factors Contributing to Cooling Retail Credit Growth
Several factors have contributed to the cooling of retail credit growth in the June quarter. Understanding these factors is crucial for predicting future trends and for businesses to navigate the evolving credit landscape.
1. Rising Interest Rates
One of the primary factors behind the slowdown in retail credit growth is the rise in interest rates. Central banks across the world have been raising interest rates to combat inflationary pressures, which has led to higher borrowing costs for consumers. With the cost of credit increasing, many consumers have become more hesitant to take on new loans or use credit cards, leading to a natural deceleration in retail credit growth.
Higher interest rates particularly affect discretionary spending financed through credit. Consumers are more likely to rethink major purchases, such as homes and vehicles, when financing becomes more expensive. As a result, mortgage and auto loan growth has been significantly impacted by rising rates.
2. Economic Uncertainty
The global economic landscape in 2024 has been marked by uncertainty. Geopolitical tensions, trade disputes, supply chain disruptions, and inflation have created a challenging environment for both businesses and consumers. In such uncertain times, consumers tend to adopt a more cautious approach to spending and borrowing.
TransUnion’s report highlights that consumer sentiment has taken a hit, with many individuals opting to save more and borrow less. This shift in consumer behavior has led to a decrease in demand for retail credit products.
3. Tighter Lending Standards
Financial institutions have also played a role in the cooling of retail credit growth. In response to the economic uncertainty and rising delinquency rates, many lenders have tightened their lending standards. This includes more stringent credit score requirements, lower credit limits, and more thorough income verification processes.
Tighter lending standards mean that fewer consumers qualify for credit, particularly those with lower credit scores. This has had a dampening effect on overall credit growth, as a significant portion of potential borrowers are being excluded from the market.
4. Consumer Debt Levels
Another contributing factor to the slowdown in retail credit growth is the high level of consumer debt. In many economies, consumers are already carrying significant debt loads, particularly in the form of mortgages and credit card debt. As a result, some consumers may be reaching their debt capacity, making them reluctant to take on additional credit.
TransUnion’s data indicates that delinquency rates on existing loans have been rising, which has prompted both consumers and lenders to be more cautious. High levels of outstanding debt can limit the ability of consumers to borrow more, leading to a natural slowdown in credit growth.
Impact on Consumers
The cooling of retail credit growth has both positive and negative implications for consumers. On one hand, slower credit growth can help prevent over-indebtedness and reduce the risk of financial instability for individuals. With fewer consumers taking on new debt, there is less likelihood of widespread defaults or financial distress.
On the other hand, the cooling of retail credit growth can limit consumers’ ability to finance major purchases or manage short-term financial needs. For example, individuals looking to buy a home or a car may find it more difficult to secure affordable financing. Additionally, consumers who rely on credit cards for everyday expenses may face higher interest rates and lower credit limits, making it harder to manage their budgets. 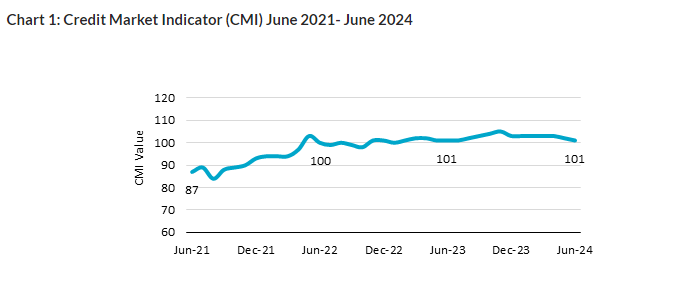 For the more information click on this link
For the more information click on this link
Impact on Businesses
For businesses, the slowdown in retail credit growth presents both challenges and opportunities. Many industries, such as retail, automotive, and real estate, rely heavily on consumer credit to drive sales. A decrease in credit growth can lead to lower sales volumes and reduced revenue for businesses in these sectors.
At the same time, businesses that offer financing options to consumers may need to adjust their strategies in response to changing market conditions. For example, companies that offer store credit or financing plans may need to tighten their credit approval processes or offer alternative payment options to attract customers.
Additionally, the cooling of retail credit growth may encourage businesses to focus on strengthening their relationships with existing customers rather than relying solely on new customer acquisition. By offering personalized financing solutions, loyalty programs, and other incentives, businesses can retain their customer base and mitigate the impact of slower credit growth.
Policy Implications
The slowdown in retail credit growth has significant implications for policymakers as well. Central banks and financial regulators must carefully balance the need to control inflation with the potential risks of stifling consumer spending and economic growth.
In the current environment, policymakers may need to consider measures to support credit growth without exacerbating inflationary pressures. This could include targeted interventions, such as providing support for first-time homebuyers or offering incentives for energy-efficient vehicle purchases.
At the same time, regulators will need to monitor the health of the financial system closely, particularly in terms of delinquency rates and the stability of financial institutions. Ensuring that banks and other lenders maintain healthy balance sheets will be critical in preventing a credit crunch that could further dampen economic activity. 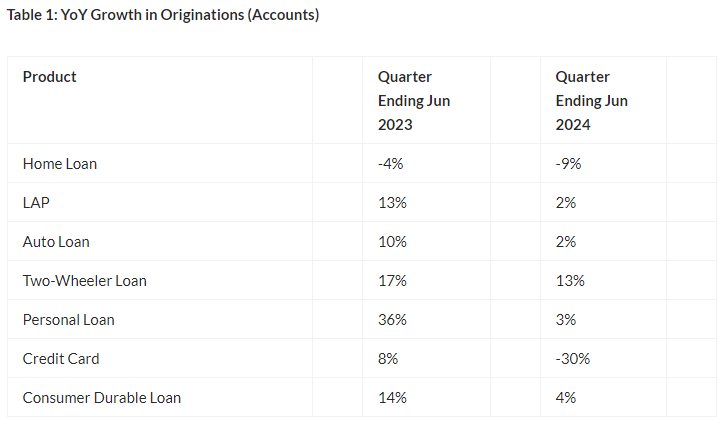 For the more information click on this link
For the more information click on this link
The Road Ahead
While the June quarter of 2024 has shown a cooling in retail credit growth, it is important to recognize that this is just one chapter in an ongoing story. The future trajectory of retail credit growth will depend on a variety of factors, including interest rates, economic conditions, and consumer sentiment.
In the short term, it is likely that retail credit growth will remain subdued as consumers and businesses adjust to the current environment. However, as inflationary pressures ease and interest rates stabilize, there may be opportunities for a rebound in credit growth.
For businesses and consumers alike, the key to navigating this period of cooling retail credit growth will be adaptability. By staying informed, managing debt responsibly, and exploring alternative financing options, individuals and businesses can weather the challenges of the current credit landscape and position themselves for future success.
Conclusion
The cooling of retail credit growth in the June quarter of 2024, as reported by TransUnion, highlights the complex interplay of factors shaping the global credit market. Rising interest rates, economic uncertainty, tighter lending standards, and high consumer debt levels have all contributed to the slowdown in credit growth. While this deceleration poses challenges for both consumers and businesses, it also offers an opportunity for more responsible borrowing and lending practices.
As we move forward, it will be essential for policymakers, financial institutions, and consumers to work together to ensure a healthy and sustainable credit environment. By balancing the need for economic growth with the risks of over-indebtedness, we can create a more resilient financial system that supports both individual prosperity and broader economic stability. ALSO READ:- UN Rights Chief Urges States to Challenge Israel over Occupation 2024




