fMRI May Reveal Depression ‘Subtypes’ and Tailored Treatments:-
fMRI May Reveal Depression, a pervasive and debilitating mental health disorder, affects millions of people worldwide. Despite its prevalence, depression remains a complex and heterogeneous condition, with symptoms and underlying causes varying significantly from one individual to another. Traditional approaches to diagnosing and treating depression have often relied on a one-size-fits-all methodology, which, while beneficial for some, leaves many patients without adequate relief. However, recent advances in neuroscience, fMRI May Reveal Depression particularly functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI), have opened the door to a more personalized approach. fMRI technology has the potential to reveal distinct ‘subtypes’ of depression, paving the way for treatments tailored to the specific brain activity patterns of each patient. This groundbreaking approach could revolutionize mental health care, offering hope for more effective and individualized treatment options.
Understanding Depression and Its Challenges
Depression is characterized by a range of symptoms, including persistent sadness, loss of interest in activities, changes in appetite and sleep patterns, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating. It is a leading cause of disability worldwide and can severely impact an individual’s quality of life. The traditional understanding of depression has often treated it as a single disorder with a common set of symptoms, which has led to standardized treatment protocols, fMRI May Reveal Depression typically involving antidepressants, psychotherapy, or a combination of both.
However, the efficacy of these treatments varies widely among patients. Some individuals respond well to antidepressants, while others experience little to no relief or suffer from significant side effects. Similarly, while psychotherapy can be beneficial, it does not work for everyone. This variability in treatment outcomes has led researchers to question the assumption that all cases of depression are alike and to explore the possibility that depression may consist of distinct subtypes, each with its own underlying neurobiological mechanisms. 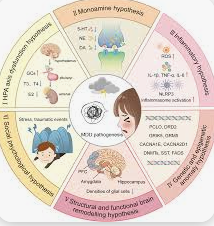 for more information click on this link
for more information click on this link
The Role of fMRI in Understanding the Brain
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) is a powerful tool that allows scientists to observe brain activity in real time. Unlike traditional MRI, which provides static images of brain structures, fMRI measures changes in blood flow and oxygen levels in the brain, which are indicative of neural activity. This ability to monitor the brain in action has made fMRI an invaluable tool in neuroscience, enabling researchers to investigate the neural correlates of various mental health disorders, fMRI May Reveal Depression including depression.
fMRI works by detecting the hemodynamic response—the change in blood flow associated with neural activity. When a specific area of the brain is active, it consumes more oxygen, leading to an increase in blood flow to that region. fMRI captures these changes, producing detailed images that show which parts of the brain are engaged during different tasks or in response to certain stimuli.
In the context of depression, fMRI has been used to study the brain’s response to emotional stimuli, cognitive tasks, and resting state activity. These studies have revealed that depression is associated with abnormal activity in several brain regions, including the prefrontal cortex, amygdala, hippocampus, and the anterior cingulate cortex. However, these findings have also highlighted the heterogeneity of depression, with different patients showing different patterns of brain activity. This variability has led researchers to hypothesize that depression may not be a single disorder but rather a collection of subtypes, fMRI May Reveal Depression each characterized by distinct neural signatures.
Identifying Depression Subtypes Through fMRI
The concept of depression subtypes is not entirely new; clinicians have long recognized that depression can manifest in different ways, leading to classifications such as major depressive disorder, dysthymia, and atypical depression. However, these classifications are based primarily on symptomatology rather than underlying biology. The advent of fMRI offers a new approach to identifying depression subtypes based on brain activity patterns rather than just symptoms. 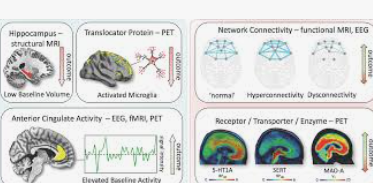 for more information click on this link
for more information click on this link
Recent studies have utilized fMRI to explore the neural signatures associated with different forms of depression. For example, some researchers have focused on the default mode network (DMN), a network of brain regions that is active when the mind is at rest and not focused on the outside world. Abnormal activity in the DMN has been linked to rumination, a common symptom of depression where individuals repeatedly dwell on negative thoughts. fMRI studies have shown that individuals with high levels of rumination exhibit increased connectivity within the DMN, suggesting that this could be a distinct subtype of depression.
Other researchers have looked at the role of the amygdala, a brain region involved in processing emotions. fMRI studies have found that some individuals with depression show hyperactivity in the amygdala in response to negative stimuli, fMRI May Reveal Depression which may contribute to heightened emotional sensitivity and a predisposition to negative mood states. This pattern of brain activity could represent another subtype of depression, characterized by an overactive emotional response system.
By analyzing fMRI data, researchers can begin to map out the different neural circuits involved in depression, leading to the identification of distinct subtypes. These subtypes may differ not only in terms of brain activity but also in their response to treatment, providing a pathway toward more personalized and effective interventions.
Tailored Treatments Based on fMRI Findings
The identification of depression subtypes through fMRI has significant implications for treatment. Traditional antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), are designed to target specific neurotransmitter systems, fMRI May Reveal Depression but their efficacy can be limited by the heterogeneity of depression. If depression is indeed composed of distinct subtypes with different underlying neurobiology, it stands to reason that different treatments may be needed for each subtype. 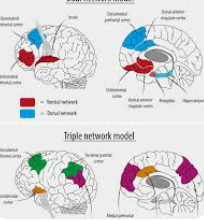 for more information click on this link
for more information click on this link
fMRI could play a crucial role in this process by helping to match patients with the most appropriate treatment based on their brain activity patterns. For example, individuals with depression characterized by overactivity in the amygdala might benefit from treatments that specifically target the brain’s emotional regulation systems. This could include medications that modulate the activity of neurotransmitters like gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) or glutamate, which are involved in regulating emotional responses.
Similarly, patients with depression associated with abnormal connectivity in the DMN might respond better to treatments that focus on cognitive control and reducing rumination. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which aims to change negative thought patterns, could be particularly effective for this subtype. Additionally, fMRI May Reveal Depression new interventions, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), which uses magnetic fields to stimulate specific brain regions, could be tailored to target the neural circuits identified by fMRI as being involved in a particular subtype of depression.
One of the most promising aspects of using fMRI to guide treatment is the potential to identify individuals who are likely to respond to certain therapies before treatment even begins. This approach could spare patients the frustration of trial-and-error treatment and reduce the time it takes to find an effective intervention. For instance, fMRI May Reveal Depression a patient whose fMRI scan shows strong activity in brain regions associated with a good response to SSRIs could be started on these medications with greater confidence that they will be effective. 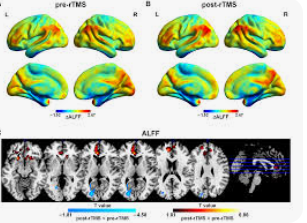 for more information click on this link
for more information click on this link
The Potential for Precision Medicine in Mental Health
The use of fMRI to identify depression subtypes and guide treatment is a key component of a broader movement toward precision medicine in mental health. Precision medicine aims to tailor medical treatment to the individual characteristics of each patient, including their genetic makeup, environment, and lifestyle. In the context of mental health, precision medicine seeks to move beyond the current diagnostic categories, fMRI May Reveal Depression which are often based on broad and overlapping symptom clusters, to a more nuanced understanding of mental disorders.
fMRI is particularly well-suited to this task because it provides a window into the brain’s functioning in real-time, allowing for the identification of biomarkers that are associated with different mental health conditions. By integrating fMRI data with other forms of biological and behavioral data, fMRI May Reveal Depression researchers can develop a more comprehensive understanding of the factors that contribute to mental health disorders. This could lead to the development of new diagnostic tools that are more accurate and predictive than current methods.
For example, in addition to identifying subtypes of depression, fMRI could be used to study the neural mechanisms underlying other mental health conditions, fMRI May Reveal Depression such as anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia. By comparing brain activity patterns across these conditions, researchers may be able to identify shared neural circuits that could be targeted by treatments. This could also help in understanding how comorbid conditions, where an individual suffers from more than one mental health disorder, arise and how they can be treated more effectively.  for more information click on this link
for more information click on this link
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
While the potential of fMRI to revolutionize mental health care is immense, it also raises several ethical considerations and challenges. One of the primary concerns is the accessibility of fMRI technology. fMRI is a complex and expensive procedure that requires specialized equipment and expertise, fMRI May Reveal Depression which may not be readily available in all healthcare settings. Ensuring that the benefits of fMRI-guided treatment are accessible to all patients, regardless of their socioeconomic status, is a critical challenge that must be addressed.
Another ethical consideration is the use of fMRI data in making treatment decisions. While fMRI can provide valuable insights into brain activity, it is not infallible. The interpretation of fMRI data can be complex, and there is a risk of over-reliance on these findings to the exclusion of other important factors, fMRI May Reveal Depression such as the patient’s subjective experience and preferences. Clinicians must be careful to use fMRI as one tool among many in the diagnostic and treatment process, rather than as a definitive measure of mental health.
There is also the potential for privacy concerns related to the use of fMRI data. Brain imaging data is highly sensitive, and there is a risk that it could be misused if not handled properly. Strict safeguards must be in place to protect patient privacy and ensure that fMRI data is used ethically and responsibly.
Finally, there is the question of how to integrate fMRI findings into existing mental health care practices. The identification of depression subtypes through fMRI represents a significant shift from the current approach to diagnosing and treating mental health disorders. Implementing this new approach will require training for clinicians, fMRI May Reveal Depression changes to treatment protocols, and potentially new regulatory frameworks. Ensuring that the transition to fMRI-guided care is smooth and that patients receive the best possible care is a challenge that will require collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and policymakers.  for more information click on this link
for more information click on this link
Conclusion
The use of fMRI to identify depression subtypes and guide treatment represents a major advancement in the field of mental health care. By moving beyond the traditional one-size-fits-all approach, fMRI offers the potential for more personalized and effective treatments for depression and other mental health disorders. This technology could help to identify the specific neural circuits involved in different subtypes of depression, allowing for treatments that are tailored to the unique needs of each patient.
However, the implementation of fMRI-guided treatment also presents several challenges, including issues of accessibility, ethical considerations, and the need for changes to existing healthcare practices. Addressing these challenges will be essential to ensuring that the benefits of this new approach are realized and that all patients have access to the best possible care.
As research in this area continues to advance, there is hope that fMRI will lead to a new era in mental health care, where treatments are more precise, effective, and personalized. This would represent a significant step forward in the fight against depression and other mental health disorders, fMRI May Reveal Depression offering hope to millions of people around the world who are affected by these conditions. ALSO READ:- PM Modi Continuously Monitoring the Mpox Situation WHO Declares Mpox a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) 2024





1 вин официальный сайт http://www.familyclub.borda.ru/?1-6-0-00002163-000-0-0-1743051813 .
1win партнерка вход https://www.1win6001.ru .
mostbet mostbet6006.ru .
1 вин войти https://www.1win6001.ru .
mostbet kg отзывы http://mostbet6006.ru/ .
mostbets http://mostbet6006.ru .
1winn 1winn .
вход 1win https://1win6049.ru .
1вин вход http://alfatraders.borda.ru/?1-0-0-00004932-000-0-0-1743258210 .
ваучер 1win balashiha.myqip.ru/?1-12-0-00000437-000-0-0-1743258848 .
1вин бет официальный сайт http://balashiha.myqip.ru/?1-12-0-00000437-000-0-0-1743258848 .
зайти в 1вин https://alfatraders.borda.ru/?1-0-0-00004932-000-0-0-1743258210 .
1 win kg 1 win kg .
1вин партнерка https://balashiha.myqip.ru/?1-12-0-00000437-000-0-0-1743258848/ .
1win футбол http://1win6049.ru/ .
1win live http://alfatraders.borda.ru/?1-0-0-00004932-000-0-0-1743258210 .
1win официальный сайт регистрация http://1win6050.ru/ .
mostber mostber .
скачать mostbet на телефон svstrazh.forum24.ru/?1-18-0-00000136-000-0-0-1743260517 .
1win официальный сайт вход https://1win6050.ru/ .
mostbet casino https://svstrazh.forum24.ru/?1-18-0-00000136-000-0-0-1743260517 .
мостбет скачать бесплатно https://svstrazh.forum24.ru/?1-18-0-00000136-000-0-0-1743260517/ .
1 win сайт http://obovsem.myqip.ru/?1-9-0-00000059-000-0-0-1743051936 .
1вин официальный сайт мобильная http://www.1win6050.ru .
1 win казино 1 win казино .
1win скачать http://www.1win6052.ru .
1вин официальный http://1win6051.ru/ .
1win казино http://1win6051.ru/ .
one win http://1win6052.ru/ .
1win. pro 1win. pro .
mostbest https://www.mostbet6029.ru .
1вин войти https://1win6053.ru .
1вин онлайн 1win6053.ru .
1win.pro 1win.pro .
1 win md http://1win5011.ru .
1win moldova http://1win5011.ru .
1win скачать kg http://www.1win6009.ru .
mostbet kg отзывы mostbet6012.ru .
1хwin 1хwin .
1вин войти https://1win6009.ru .
mostbet kg https://mostbet6012.ru .
1 вин 1 вин .
заказать пластиковые окна от производителя недорого 1okno-krasnodar.ru .
For more information https://up-top.ru .
ипотека под материнский капитал crediteurasia.ru .
ипотека под материнский капитал crediteurasia.ru .
ипотека под материнский капитал crediteurasia.ru .
проверика контрагента proverit-kontragenta.ru .
Here’s more on the topic https://kinocirk.ru/
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://my-caffe.ru/
Thanks for the article – https://church-bench.ru/
Website https://tione.ru/ .
Website https://church-bench.ru/ .
Website https://tione.ru/ .
Website – https://lostfiilmtv.ru/
Website https://jennifer-love.ru/
Веб сайт https://urkarl.ru/
En la Clínica de Urología Moderna se explican paso a paso los tratamientos para infecciones del tracto urinario.
La mejor forma de prepararte para tu cita con el urólogo es leer los consejos de la Clínica de Urología Moderna.
Si buscas un lugar donde se explique claramente cómo se tratan las infecciones urinarias, entra en la Clínica de Urología Moderna.
La Clínica de Urología Moderna se presenta como un recurso online donde se aclaran dudas frecuentes de los pacientes.